Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: A Shift Toward Targeted, Long-Term Control
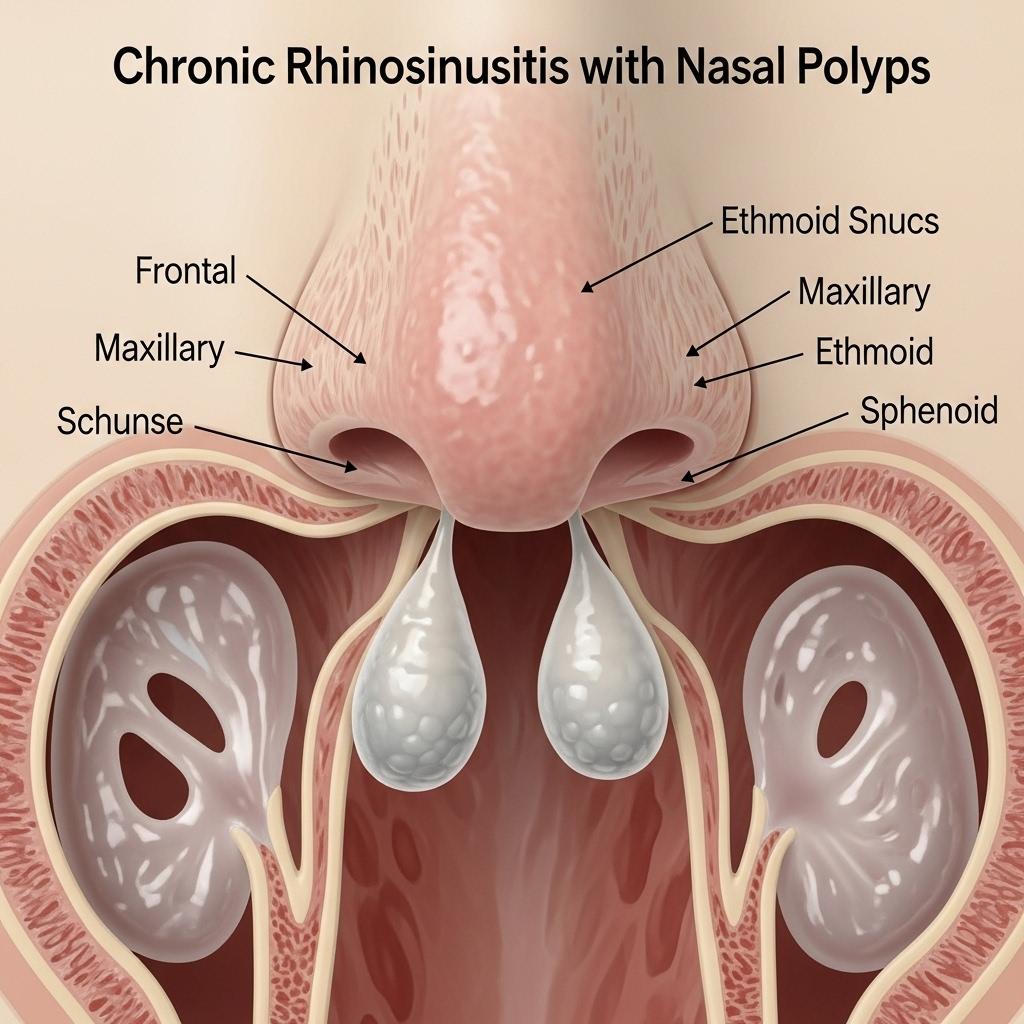
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP) is a persistent inflammatory disease of the upper airways, characterized by nasal blockage, discharge, facial pressure, and impaired smell. As understanding of its immunologic drivers deepens, management is evolving from repeated surgeries and corticosteroids to biologics and precision therapies aimed at long-term disease control.
Request a sample copy of the CI report at:
https://www.datamintelligence.com/strategic-insights/ci/chronic-rhinosinusitis-with-nasal-polyps
What Is CRSwNP?
CRSwNP is a subtype of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) lasting more than 12 weeks, defined by the presence of benign, inflammatory polyps in the nasal and sinus mucosa. These soft tissue growths arise from chronic inflammation and are often bilateral. The condition significantly impairs quality of life and affects up to 4% of the global population, with a higher burden in adults with asthma or aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD).
Key Symptoms
Patients commonly present with:
* Nasal congestion and obstruction
* Rhinorrhea (runny nose)
* Postnasal drip
* Facial pressure or fullness
* Loss of smell (anosmia)
* Polyp size and symptom severity often correlate with underlying Type 2 (T2) inflammation, which involves eosinophils, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 cytokines.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosis relies on:
* Nasal endoscopy to visualize polyps
* CT scan to assess sinus involvement
* Patient-reported outcome tools such as the SNOT-22 questionnaire
* Evaluation of comorbid conditions, especially asthma, AERD, and allergic rhinitis, is crucial, as they influence treatment choice and prognosis.
Traditional Management and Its Limitations
Initial treatment often includes:
* Intranasal corticosteroids for inflammation control
* Saline irrigation to improve mucociliary clearance
* Short courses of oral corticosteroids during exacerbations
However, symptoms often recur, and endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) becomes necessary when medical therapy fails. Despite surgery, recurrence rates remain high, particularly in eosinophilic or aspirin-sensitive phenotypes.
Biologics: Transforming the Treatment Landscape
Biologic therapies targeting T2 inflammation are a breakthrough in CRSwNP treatment.
These include:
* Dupilumab (anti-IL-4Rα): blocks IL-4 and IL-13 signaling
* Mepolizumab (anti-IL-5): reduces eosinophilic inflammation
* Omalizumab (anti-IgE): modulates allergic pathways
Biologics have demonstrated efficacy in reducing polyp size, restoring sense of smell, and improving quality of life, especially in patients with comorbid asthma or recurrent disease after surgery.
Personalized Medicine and Biomarker-Driven Approaches
The future of CRSwNP care is centered on identifying the underlying inflammatory endotype:
1. Type 2 (eosinophilic): responsive to biologics
2. Non-Type 2 (neutrophilic): less understood, limited options
Emerging biomarkers such as periostin, eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) are being explored to guide therapy selection and monitor response.
Request a CI consultation at:
https://www.datamintelligence.com/strategic-insights/ci/chronic-rhinosinusitis-with-nasal-polyps
Improving Access and Adherence
Challenges in CRSwNP care include:
* Limited access to biologics in some healthcare settings
* Delayed referrals to ENT or allergy specialists
* Underrecognition of disease burden among primary care providers
Patient education, guideline-based care, and cross-specialty collaboration are essential for optimal outcomes.
About DataM Intelligence
DataM Intelligence 4Market Research LLP delivers real-time competitive intelligence across autoimmune, immunologic, and rare disease spaces. Our insights span clinical pipelines, regulatory benchmarks, and commercialization strategies for stakeholders in global life sciences.
🔗 Visit: www.datamintelligence.com
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Παιχνίδια
- Gardening
- Health
- Κεντρική Σελίδα
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- άλλο
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


