How to Manage Chronic Lung Infections in Non-CF Bronchiectasis
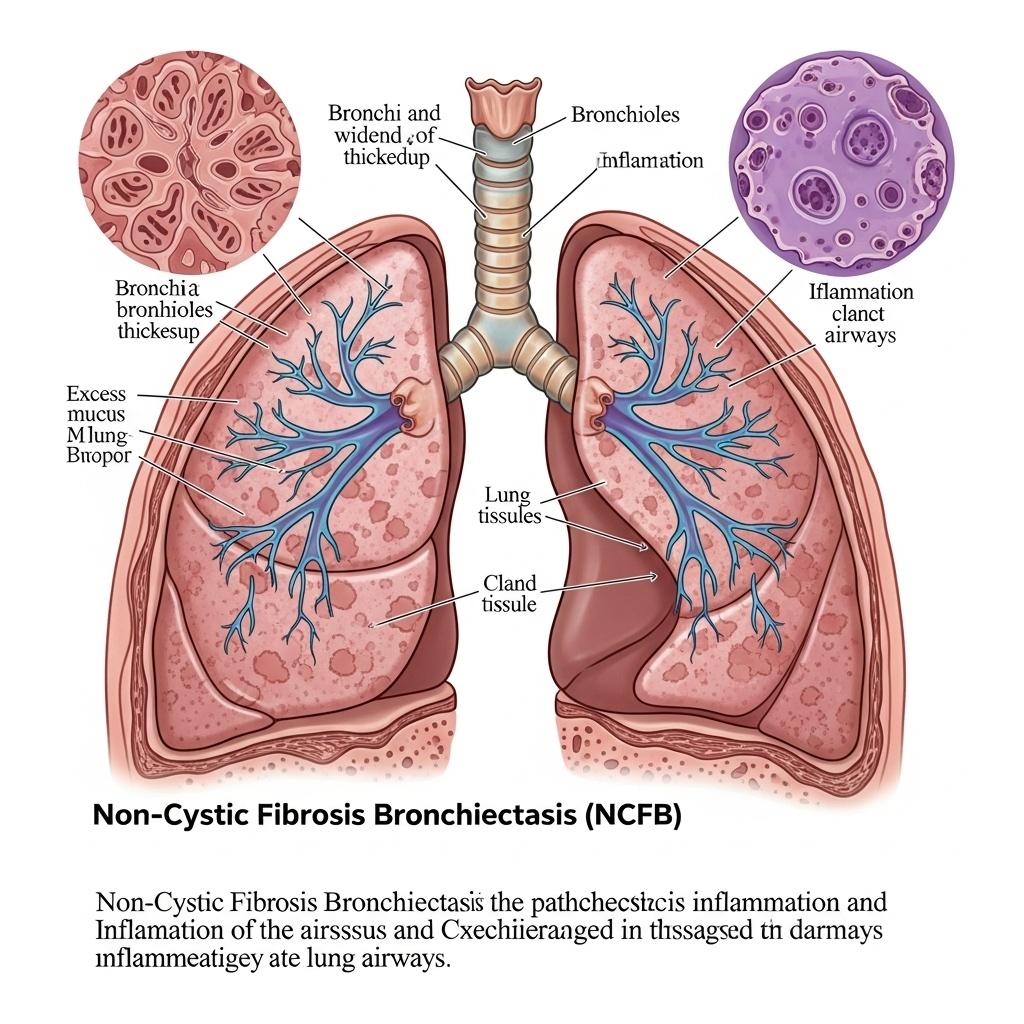
Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis (NCFB), a chronic and progressive airway condition, has long existed in the shadow of more prominent pulmonary diseases. Characterized by irreversible bronchial dilation, mucus buildup, and recurrent infections, NCFB leads to chronic cough, sputum production, and significant morbidity. While distinct from cystic fibrosis (CF), NCFB requires equally aggressive management. Recent advances in imaging, microbiology, and targeted therapy are helping clinicians better understand, classify, and treat this complex condition.
Request a sample copy of the CI report at:
https://www.datamintelligence.com/strategic-insights/ci/idiopathic-hypersomnia-i
Understanding the Disease Pathophysiology
In NCFB, structural damage to the bronchial walls causes permanent widening of the airways. This distortion impairs mucus clearance, creating an environment prone to chronic bacterial colonization and inflammation. Over time, this leads to a cycle of infection, inflammation, and further airway injury.
Unlike CF, which results from a genetic mutation in the CFTR gene, NCFB may arise from multiple causes, including:
* Prior severe lung infections (e.g., tuberculosis, pneumonia)
* Primary immunodeficiencies
* Autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis)
* Ciliary dysfunction (e.g., primary ciliary dyskinesia)
* Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
* Idiopathic causes (30–40% of cases remain unexplained)
Diagnosis and Disease Evaluation
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) remains the gold standard for diagnosing bronchiectasis, revealing airway dilation, lack of tapering, and bronchial wall thickening.
Additional investigations include:
* Sputum culture to identify chronic pathogens like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, or Moraxella catarrhalis
* Pulmonary function tests to assess airflow limitation
* Immunoglobulin panels to detect immune deficiencies
* Screening for underlying causes such as ABPA or ciliary dysfunction
* Frequent exacerbations and poor quality of life often point to advanced disease requiring more intensive management.
Current Management Strategies
NCFB is managed through a combination of airway clearance, infection control, and inflammation reduction.
Key components include:
1. Airway Clearance Techniques (ACTs): Chest physiotherapy, oscillatory PEP devices, and postural drainage help mobilize secretions.
2. Inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids: For patients with coexisting asthma or COPD.
Antibiotic therapy:
* Oral or IV antibiotics during acute exacerbations
* Inhaled antibiotics (e.g., tobramycin, colistin) for chronic Pseudomonas infections
* Macrolide maintenance therapy (e.g., azithromycin) for immunomodulation and infection prevention
* Pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking cessation, and influenza/pneumococcal vaccination are also critical components of long-term care.
Precision Therapy and Emerging Approaches
The evolving understanding of NCFB’s heterogeneity is paving the way for phenotype-guided treatment.
Clinical trials are evaluating:
* Neutrophil elastase inhibitors
* CFTR modulators in patients with CFTR mutations but no cystic fibrosis
* Long-acting inhaled antibiotics with better lung deposition
* Biologics (e.g., anti-IL-5 agents) for patients with eosinophilic airway inflammation
* Anti-inflammatory peptides and gene expression modulators
These targeted approaches aim to reduce disease progression and hospitalization rates while improving quality of life.
Challenges and Global Disparities
Despite increasing recognition, NCFB remains underdiagnosed and undertreated in many regions. Global barriers include:
1. Limited access to diagnostic HRCT and microbiology
2. Absence of standardized treatment protocols in primary care
3. Low awareness among general practitioners and pulmonologists
4. Underrepresentation in clinical trials
Collaborative registries and education initiatives are helping close the gap and inform national treatment strategies.
Request a CI consultation at:
https://www.datamintelligence.com/strategic-insights/ci/idiopathic-hypersomnia-ih
Prognosis and Patient Outlook
While NCFB is not curable, early diagnosis and aggressive, personalized care can significantly reduce exacerbations and preserve lung function.
Factors associated with worse outcomes include:
* Chronic Pseudomonas colonization
* Frequent exacerbations (≥2/year)
* Low baseline lung function (FEV1 <50%)
* Hemoptysis
* Comorbidities (e.g., COPD, immunodeficiency)
Improving access to multidisciplinary care and new therapeutics remains a public health priority.
About DataM Intelligence
DataM Intelligence 4Market Research LLP delivers real-time competitive intelligence across respiratory, immunologic, and rare disease domains. Our insights span *** pipelines, clinical trial tracking, regulatory milestones, and commercial strategy, helping global healthcare stakeholders make informed decisions.
🔗 Visit: www.datamintelligence.com
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Juegos
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


