Bacterial Infections: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
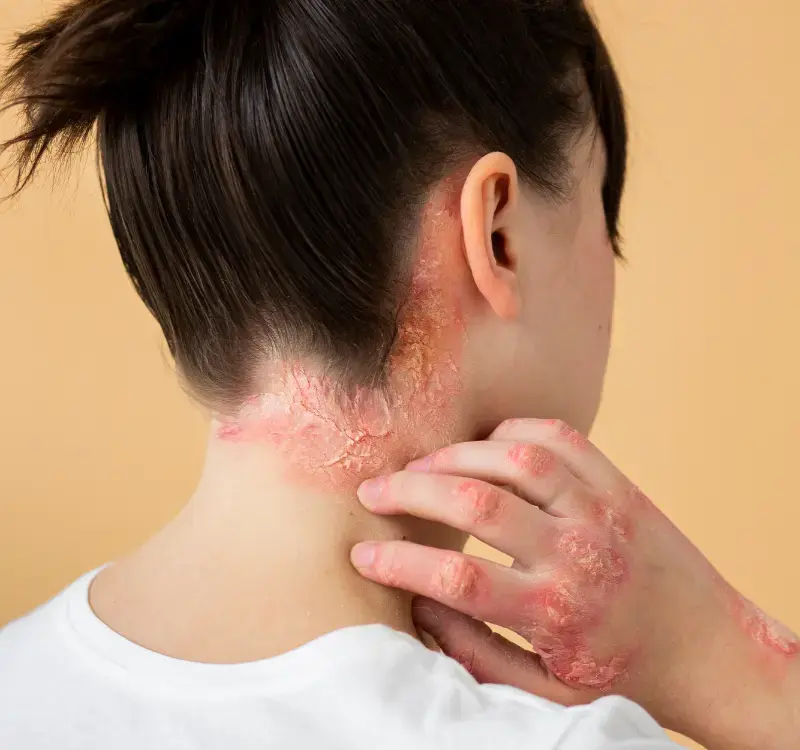
Bacterial infections are a common health concern that can affect various parts of the body. These infections are caused by harmful bacteria that multiply and disrupt normal bodily functions. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments of bacterial infections is essential to managing and preventing their spread. One of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for treating bacterial infections is Cephalexin wholesale.
Symptoms of Bacterial Infections
The symptoms of bacterial infections can vary depending on the affected area of the body. However, some common signs include:
- Fever: A raised body temperature is often a sign of infection.
- Pain: Infected areas may become painful, swollen, and tender to touch.
- Redness and Inflammation: Infections can cause redness and swelling in the affected area, particularly on the skin.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak is a common symptom of infection.
- Coughing and Sore Throat: In respiratory infections, symptoms like coughing, sore throat, and shortness of breath may appear.
- Digestive Issues: Bacterial infections affecting the digestive tract may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
Causes of Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are caused by the introduction of harmful bacteria into the body. These bacteria can enter the body through cuts, wounds, respiratory droplets, contaminated food or water, and other sources. Common causes include:
- Contact with Infected Individuals: Bacteria spread easily from person to person through direct contact or airborne droplets.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more vulnerable to infections.
- Poor Hygiene Practices: Lack of proper handwashing or cleanliness can facilitate bacterial growth.
- Contaminated Food or Water: Eating undercooked food or drinking contaminated water can introduce harmful bacteria.
- Invasive Medical Procedures: Surgery or use of medical devices like catheters can increase the risk of infection.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes or heart disease can make individuals more susceptible to infections.
Role of Cephalexin in Treating Bacterial Infections
Cephalexin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic that belongs to the cephalosporin class. It is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, which eventually leads to the destruction of the bacteria. Cephalexin is effective against a variety of bacterial strains, making it a go-to treatment for several conditions.
Common Uses of Cephalexin
- Respiratory Infections: Cephalexin can treat infections like pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: It is commonly used to treat infections such as cellulitis, impetigo, and wound infections.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Cephalexin can be used to treat bacterial infections of the urinary system.
- Bone and Joint Infections: In some cases, Cephalexin is used for bone infections like osteomyelitis.
- Ear Infections: It can also be prescribed for bacterial ear infections (otitis media).
Treatment with Cephalexin: How It Works
Cephalexin works by preventing bacteria from forming a cell wall, which is essential for their survival and replication. Without a cell wall, the bacteria cannot maintain their shape or integrity, ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism is effective against both Gram-positive and some Gram-negative bacteria, which allows Cephalexin to be useful for treating a wide variety of infections.
How to Take Cephalexin
Cephalexin is typically available in the form of tablets, capsules, and liquid suspensions. It is important to follow the doctor's instructions for dosage and frequency. Generally, the medication is taken every 6 to 12 hours, with or without food. The complete course of treatment should always be followed to ensure the infection is fully treated and to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Side Effects of Cephalexin
Here’s a table summarizing the side effects of Cephalexin:
| Side Effect Category | Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Common Side Effects | Gastrointestinal Issues: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain |
| Allergic Reactions: Mild rash, itching | |
| Headache and Dizziness: Lightheadedness or headaches | |
| Fatigue and Weakness: General tiredness or weakness | |
| Yeast Infections: Oral thrush or vaginal yeast infection | |
| Serious Side Effects | Severe Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis): Difficulty breathing, swelling of face/tongue, severe rash |
| C. diff-associated Diarrhea: Severe diarrhea (with blood/mucus), cramping, fever | |
| Severe Skin Reactions: Blistering, peeling, or severe rashes | |
| Kidney Issues: Changes in urination, swelling in ankles/feet, fatigue | |
| Hematologic Effects: Unusual bruising/bleeding, pale skin, dizziness |
This table provides a clear distinction between common side effects and serious side effects of Cephalexin. If any serious side effects occur, it's important to seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Bacterial infections can vary in severity, but understanding their symptoms, causes, and the role of antibiotics like Cephalexin in treatment is vital for effective management. Cephalexin is an essential antibiotic in fighting a broad range of bacterial infections, and following prescribed treatment regimens is crucial to ensure successful recovery. As with all medications, it is important to use Cephalexin as directed and report any side effects to a healthcare provider.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


