Understanding Side Effects for Bone Marrow Donors
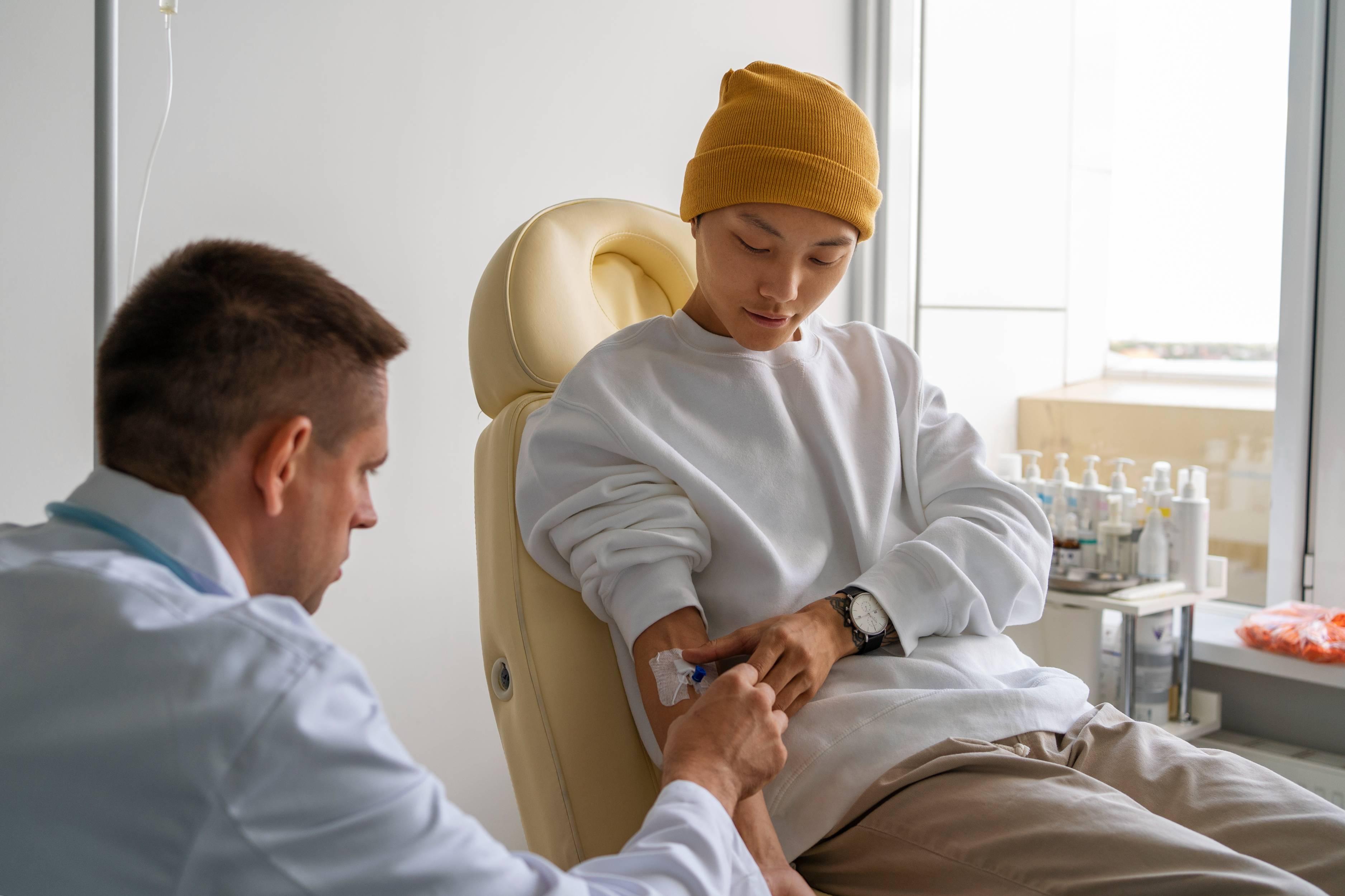
A bone marrow transplant (BMT) is a fairly routine procedure to replace the marrow that is not working properly with a new one, which is still functioning. Marrow is that part of the body that produces red and white blood cells as well as platelets, and it also helps with ACL reconstruction surgery. This blog is about the donor's side of the bone marrow transplant, including its types, risks, recovery, and the best hospitals.
If you want to have healthy bone marrow, then eat a balanced diet, take enough vitamins (including B12 and folate), and do not smoke or drink alcohol. The side effects of bone marrow, after a transplant, are symptoms such as nausea, hair loss, and infection.
What is a Bone Marrow Transplant?
A bone marrow transplant is a medical operation that changes the patient's bone marrow, which is either damaged or affected by disease, with a healthy one. Bone marrow is the part of the bones that is soft and spongy and is the place where the body produces and keeps the blood cells. When the bone marrow is injured, it produces fewer blood cells that are necessary for the immune system.
Donor Side Effects of Bone Marrow Transplantation
Bone marrow transplants are also referred to as stem cell transplants. Side effects for a donor of a bone marrow transplant are pain, bruising, and soreness. These symptoms result from bone marrow harvesting, or are muscle aches, headache, and tiredness associated with peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) donation. However, temporary side effects (such as hypocalcemia and bone pain) associated with the mobilizing agent (eg, G-CSF) may be experienced by some patients. Serious complications are rare but may include anesthesia reactions, nerve damage, or infection.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplant
There are mainly two types of bone marrow transplant: autologous and allogeneic
-
Autologous transplants refer to the use of the patient's own stem cells by doctors. Since the risk of rejection is minimized, it is a typical treatment in the case of those types of cancers such as lymphoma or myeloma.
-
In allogeneic, a higher chance that the disease might come back. Allogeneic transplants use donor cells. These can actually cure some diseases, like leukemia, by building a brand-new immune system. But they’re trickier-there’s a risk the body rejects the new cells, or the new immune cells attack the patient’s tissues (that’s graft-versus-host disease).
Need for Bone Marrow Transplant
Bone marrow can make red blood cells, white blood cells , and platelets. Individuals have bone marrow transplants to substitute the damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy blood stem cells. This operation is the only known cure for several diseases, including immune deficiency disorders, serious blood conditions such as sickle cell anaemia and aplastic anaemia, and certain cancers such as leukaemia and lymphoma.
Risks to Donors after Bone Marrow Transplant
Bone marrow transplant donors have some risks, including pain where the marrow is removed, flu-like symptoms (for stem cell donors), and infection. The risks of anesthesia during bone marrow removal are minimal. Donors can also have fatigue, emotional distress, and transient bone or muscle aches. Although these complications are rare, they should be taken seriously, as most recipients do recover quickly.
Recovery Time Side Effects of Bone Marrow Transplant
When your bone marrow transplant takes a much longer time for recovery, the risk of side effects or complications is high for patients. After the transplantation, there are two most common issues:
-
The risk of infection is higher and lasts longer than in transplants using your own stem cells
-
And the particular complication of donor transplants, called graft versus host disease
Best Hospital for Bone Marrow Transplant in India
When it comes to selecting a hospital in India for a bone marrow transplant. We have several hospitals in many states in India for the best treatment to patients, like Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon, Medanta – The Medicity in Gurgaon, Apollo Hospitals in Delhi and Chennai, and BLK-MAX Hospital in Delhi. These long-established centers have been noted for experienced doctors and superior success rates.
Success Rate of Bone Marrow Transplant
Success rates for BMT vary widely depending on the type of transplant. It also depends on the condition of the patients and their health in general; they have improved a lot. For autologous transplants, the success rate is about 90 to 95%; for allogeneic transplants, 70 to 90% for half-matched donors, and 80 to 90% for fully matched donors. For certain diseases, such as some blood cancers (aplastic anemia), the cure rate can be as high as 80–90%, and survival rates reaching 50–80% or more, particularly if past the first 5 years, as long as there is no evidence of disease recurrence.
Conclusion
A bone marrow transplant is the only hope for those patients with these diseases to extend their life expectancy and be able to live a life with family. Adds ‘there's an opportunity with the second chance at life to rebuild a healthy immune system. Donors are the key that unlocks a life-saving cure, giving patients not only the chance to live but also the hope for a healthier tomorrow. In combination with innovation in treatment, increased success rates, and improved supportive care, bone marrow transplants are still the most powerful life-saving interventions available in the medical field.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


